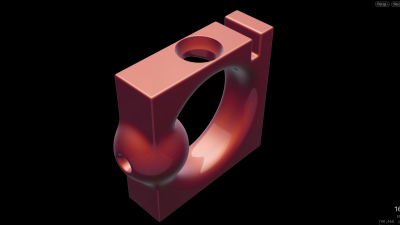

In Development: A simple CSG tool which stacks smooth boolean operations such as union, subtract and intersect on solid geometries, ie. boxes and spheres.
Solid objects: Sphere, Box, Tube, Capsule, Torus, Cone.
Boolean operations: Union, Subtract, Intersect.
Shapes: Sharp, Round, Chamfer, Columns, Stairs, Pipe.
Transformation: Size, Position, Rotation.
Repetition: None, Line, Grid, Radial, Mirror.
Volume wrangle on a SDF volume. A loop is feeding menu input from a multiparm block into signed distance functions and combines them using boolean operations. sd and op are wrapper functions.
// SIGNED-DISTANCE FUNCTIONS
function float sd_sphere(vector xyz, pos; float r){
float dist = length(xyz - pos) - r;
return dist;
}
function float sd_box(vector xyz, pos, size){
vector q = abs(xyz - pos) - size;
float dist = length(max(q, 0.0)) + min(max(q.x, max(q.y, q.z)), 0.0);
return dist;
}
function float sd_capsule(vector xyz, pos, size){
pos = xyz - pos;
pos.y -= clamp(pos.y, 0.0, size[1]);
return length(pos) - size[0];
}
function float sd(int type; vector xyz, pos, size){
float dist = 0.0;
if(type == 0) dist = sd_sphere(xyz, pos, size[0]);
else if(type == 1) dist = sd_box(xyz, pos, size);
else dist = sd_capsule(xyz, pos, size);
return dist;
}
// BOOLEAN OPERATIONS
function float op_union( float d1, d2) { return min(d1, d2); }
function float op_subtract( float d1, d2) { return max(-d1, d2); }
function float op_intersect( float d1, d2) { return max(d1, d2); }
function float op_union_sm( float d1, d2, k ) {
float h = clamp( 0.5 + 0.5*(d2-d1)/k, 0.0, 1.0 );
return lerp( d2, d1, h ) - k*h*(1.0-h); }
function float op_subtract_sm( float d1, d2, k ) {
float h = clamp( 0.5 - 0.5*(d2+d1)/k, 0.0, 1.0 );
return lerp( d2, -d1, h ) + k*h*(1.0-h); }
function float op_intersect_sm( float d1, d2, k ) {
float h = clamp( 0.5 - 0.5*(d2-d1)/k, 0.0, 1.0 );
return lerp( d2, d1, h ) + k*h*(1.0-h); }
function float op(int comb; float d_0, d_1, r){
float dist = 0.0;
if(r < 1e-3){
if (comb == 0) dist = op_union (d_0, d_1);
else if (comb == 1) dist = op_subtract (d_0, d_1);
else dist = op_intersect (d_0, d_1);
}
else{
if (comb == 0) dist = op_union_sm (d_0, d_1, r);
else if (comb == 1) dist = op_subtract_sm (d_0, d_1, r);
else dist = op_intersect_sm (d_0, d_1, r);
}
return dist;
}
// SCENE ASSEMBLY
float dist_scene = 0.0;
for(int i = 0; i <= chi('objects'); i++){
string num = itoa(i);
int type_obj = chi('type_obj' + num);
int type_op = chi('type_op' + num);
vector rot = set(chf('rx' + num), chf('ry' + num), chf('rz' + num));
vector xyz = v@P * maketransform(0, rot);
vector size = set(chf('sx' + num), chf('sy' + num), chf('sz' + num));
vector pos = set(chf('px' + num), chf('py' + num), chf('pz' + num));
float r_sm = chf('sm' + num);
float d = sd(type_obj, xyz, pos, size);
if(i == 0) dist_scene = d;
else dist_scene = op(type_op, d, dist_scene, r_sm);
}
f@d = dist_scene;
Distance functions by Inigo Quilez: https://iquilezles.org/articles/distfunctions/
More resources:
https://iquilezles.org/articles/
https://mercury.sexy/hg_sdf/
http://jamie-wong.com/2016/07/15/ray-marching-signed-distance-functions/